PCB delamination refers to the division of printed circuit boards into multiple layers, each of which uses a different circuit design to meet the needs of modern electronic equipment for complex circuits. This design method not only improves the functionality of the board, but also reduces the difficulty of wiring, making complex layouts that are difficult to achieve with single-layer boards possible in multi-layer designs.
The delamination principle of PCB circuit boards uses specific dielectrics and plating to electrically insulate and interconnect multiple layers to optimize circuit layout and functionality. This layered design allows electronic components to be laid out more compactly, reduces line crossings, ensures the quality and reliability of signal transmission, and improves the shielding of electromagnetic interference.
Generally speaking, PCB circuit boards usually contain a signal layer, a power supply layer and a ground layer. The signal layer is mainly used to transmit signals, the power supply layer provides power to the circuit components, and the ground layer is used to form a ground plane to stabilize the interference between the signal and the power supply. In some complex applications, other functional layers can be considered to be added,such as clock layers, shielding layers, etc.
How to perform PCB delamination?
1.Layering program
When designing a circuit board, you need to choose a layering scheme based on the needs and characteristics of the board. Common layering schemes are as follows:
(1) Single-sided board: all circuit components are on the same side,suitable for simple circuits.
(2) Double-sided board: pcb components are arranged on both sides and connected in the middle by over-holes.
(3) Four-layer board: the outer layer is the signal layer,the inner layer is the power supply and ground layer, and the middle is connected by an over-hole.
(4) Multi-layer board: composed of signal layer,power supply layer, ground layer, etc., with interconnecting layers or via holes in the middle.
2.Distribution of components
The layering process requires the layout of components according to the actual needs of the circuit. The distribution of components can be automatically adjusted through the software, can also be realized through manual adjustment. In the layout process, you need to pay attention to the distance between the components and impedance matching and other issues.
3.Wiring rules
The development of wiring rules is a very important step in the layering of PCB design. Wiring rules include circuit alignment direction, line width, spacing, grounding, interface, signal integrity and other elements. Reasonable wiring rules can improve the performance of the circuit board to ensure the quality of the circuit signal transmission.
The presence of delamination electronics helps to improve the conductivity of printed circuit boards. In the wiring process of PCBs, the conductive layer consists of metals (e.g. copper) and the delaminated electrons in these metals are able to move freely to form current pathways. This free electron mobility allows PCBs to exhibit good conductivity in high-frequency and high-density electronic applications, thereby meeting the requirements of modern electronics for circuit transmission speeds.
In printed circuit boards, the activity of delamination electronics not only affects the conductivity, but also closely related to thermal management. Electronic components in the working process will produce heat, and the movement of the delamination of the electronic can effectively dissipate heat, reduce the operating temperature of the circuit. This is essential to ensure the stability and prolong the service life of the circuit board, especially in high-power and high-frequency application environments.
In multilayer printed circuit boards, the connection between layers usually relies on the machining of microblind and through holes, and the free movement of delamination electronics can support the reliability of this connection. The nature of the delamination electronics ensures stable transmission of electrical signals as they propagate between different layers. In addition, good delamination electron properties help to increase the transmission rate and quality of signals and reduce signal loss.
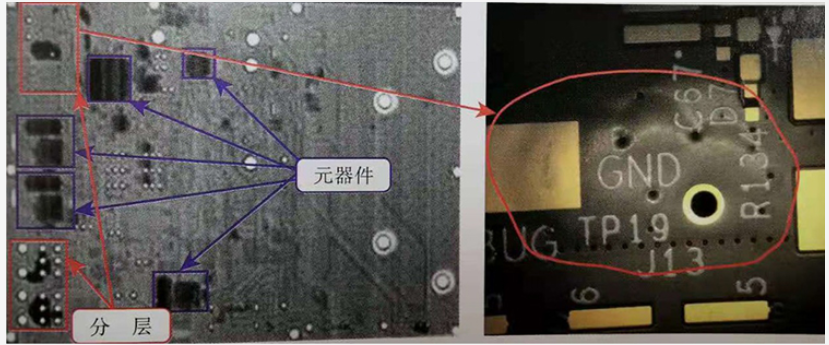
pcb delamination considerations
1.Basic principles of layered design
In the design of multilayer PCB,reasonable layering is very important.Usually,the design will contain the signal layer, power plane and ground plane, such layering can ensure the stability of electrical performance and signal integrity.
2.Layout of Signal Lines and Return Layers
Each signal line should have a corresponding return layer,also known as an image layer.This is to provide a reliable reference level,ensure signal integrity and reduce noise interference. This design is especially suitable for circuits with high speed signal transmission to reduce problems caused by signal distortion and reflections.
3.Layout of Power and Ground Layers
The power and ground layers are located as close as possible and preferably adjacent to each other,which improves power integrity and reduces electromagnetic interference (EMI). During design,special attention should be paid to the spacing between the power and ground layers to ensure good power distribution and a stable operating environment.
4.Selection of layers
Choosing the right number of layers is the key to ensure PCB performance.According to the design requirements, the rational planning of layer structure is carried out to meet the requirements of signal integrity,power distribution and electromagnetic interference control. Multi-layer PCB design can provide higher functional density, but the designer needs to balance performance and production complexity.
5.Thermal layer design
In multi-layer PCBs,thermal design is equally important.A proper thermal layer can help manage the heat in the board, reduce the risk of temperature rise, and ensure that the components operate within the normal temperature range.This not only extends the life of the board, but also improves overall performance.
6.Importance of Material Selection
When designing a PCB,the choice of materials also has a significant impact on the performance of the circuit.The electrical,thermal and mechanical properties of the material must be considered to ensure that the material selected can effectively support the functional requirements of the design.High quality materials can enhance the reliability and performance of the board.
7.Handling of High Frequency Signals
When dealing with high-speed or high-frequency signals, it is especially important to carefully design the signal layer layout and impedance matching to prevent signal attenuation and interference. The design of the signal layer should give priority to the signal transmission path to ensure that the short circuit and reduce signal delay.
In short,PCB delamanition is an important part of printed circuit board design, the effectiveness of which directly affects the board's performance, reliability and functionality expansion.