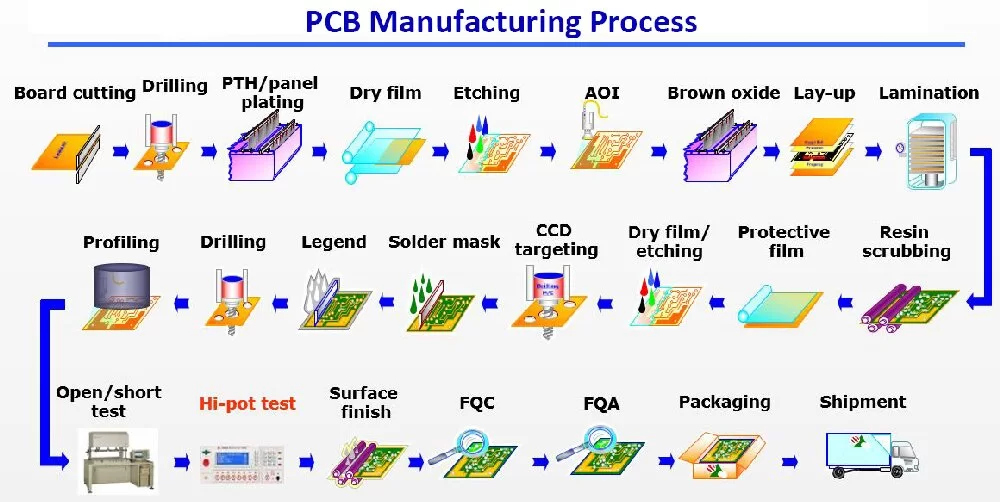
The industrial PCB manufacturing process is a complex and precise operation, involving multiple stages and technical treatments from initial design to the final product. As the backbone of the electronics industry, the quality of PCBs directly impacts the performance and reliability of electronic devices. This article delves into every stage, providing a detailed understanding of its key steps and technical nuances.
The industrial PCB manufacturing process begins with design and planning. The performance and functionality of the final product are determined at this stage. Engineers use professional design software such as Altium Designer or Cadence to create layouts and routing diagrams for the circuit board. These design files must be highly accurate, as any errors can lead to failures in subsequent manufacturing stages. Additionally, the design phase involves considering production costs, material selection, and future Design for Manufacturing (DFM) requirements.Next comes material selection and preparation. PCBs typically consist of multiple layers of copper foil and insulating materials like FR4. Manufacturers prepare appropriate substrate materials and cut them to specified dimensions according to design requirements. Parameters such as material thickness, conductivity, and heat resistance must meet specifications to ensure the final product performs reliably in various applications.
The critical steps are pattern transfer and etching. At this stage, the circuit design pattern is transferred onto the copper layer using photolithography techniques. The unprotected copper is then chemically etched away, leaving only the desired circuit patterns. This process demands high precision and cleanliness to prevent even the slightest errors from affecting circuit performance.Drilling and plating follow. For multilayer PCBs, drilling creates vias that connect layers for signal transmission. These holes are plated with conductive material during the plating process to establish reliable electrical connections. High-precision drilling equipment and stringent quality control ensure that each hole's position and dimensions align with the design requirements.
industrial PCB manufacturing process
The industrial PCB manufacturing processalso includes pad and surface treatment. At this stage, the pads on the circuit board are coated with flux or a plating layer to facilitate component soldering. This step not only affects soldering quality but also influences the PCB’s corrosion resistance and lifespan. Common surface treatment methods include electroless nickel immersion gold (ENIG), silver immersion, and hot air solder leveling (HASL).Once the above steps are completed, the PCB moves to the inspection and testing stage. Testing is a crucial part of the industrial PCB manufacturing process, identifying and rectifying potential defects. Common testing methods include Automated Optical Inspection (AOI), Automated X-ray Inspection (AXI), and flying probe tests. These tests ensure the electrical performance and mechanical integrity of the PCB, preventing defective products from reaching the market.The final step is assembly and packaging. During this stage, tested PCBs are assembled into final electronic devices or packaged directly for delivery to customers. This stage often includes anti-static handling and environmental protection measures to ensure the PCBs are not damaged during shipping and storage.
One of the most important considerations in the industrial PCB manufacturing process is scaling for large-scale production. Modern factories rely heavily on automation to meet demand while maintaining consistent quality. High-speed pick-and-place machines, reflow soldering systems, and inline inspection equipment are crucial for achieving production goals without compromising on precision. Automation not only reduces labor costs but also enhances the reproducibility of the manufacturing process, ensuring that each PCB meets stringent quality standards.As industries move toward greener practices, sustainability has become a focus in the PCB manufacturing process. Efforts to reduce waste and recycle materials, such as copper and solvents, are being implemented globally. Some manufacturers have started adopting eco-friendly etching solutions and water treatment systems to minimize environmental impact. These advancements not only benefit the planet but also align with the growing consumer and regulatory demand for environmentally responsible products.
In conclusion, the industrial PCB manufacturing process is a multidisciplinary and technologically intensive engineering effort. Each step, from design to the finished product, plays a critical role in determining the performance and quality of the PCB. By continuously improving technologies and optimizing processes, manufacturers can enhance product quality and meet the ever-changing demands of the market. From embracing automation for efficiency to integrating sustainable practices for the future, the PCB manufacturing industry continues to evolve, delivering cutting-edge solutions to the world of electronics.