Thermal clad PCBs provide the minimum thermal impedance while conducting heat more effectively than standard printed circuit boards.
Thermal clad PCB, Also known as metal core PCB, it is mechanically more robust compared to directly bonding copper and thick film ceramic structures.
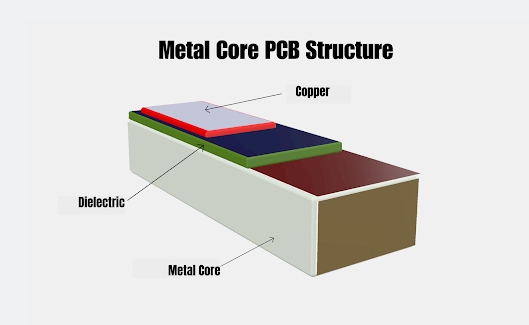
Thermal clad PCB
Thermal clad PCB, also known as Insulated Metal Substrate PCB or Metal Clad PCB, is a type of PCB that uses metal core materials such as aluminum or copper to dissipate heat.
Metal coated printed circuit boards are used for applications that require efficient heat dissipation, such as LED lighting, motor controllers, inverters, automotive electronics,
power supplies, motor controllers, etc.
The applications of Thermal clad PCBs include high-temperature applications such as power conversion, LED applications, solid-state relays, solar receivers, heat rails, and motor drivers.
Thermal clad PCB provides a simple method for achieving thermal stability. The metal core removes excess heat through substrate conduction.
To improve efficiency, an additional heat sink can be added to the metal core.
Thermal clad PCBs use aluminum or copper as the metal core for heat dissipation, thereby extending the lifespan of the PCB.
The metal core provides a low thermal resistance path for heat to flow from high-power components.
Standard printed circuit boards do not have a specific mechanism to handle high temperatures and power levels, so they cannot be used for such applications.
The thermal management capability of Thermal clad PCB depends on various factors, such as the thickness of the metal core, the thermal conductivity of the metal core material,
and the thermal conductivity of the dielectric. These PCBs provide effective solutions for applications that require efficient heat dissipation, high temperature, and high power performance.
Its effective thermal management, mechanical stability, and reliability make it the best choice for high-power electronic products.
High power electronic components may generate excessive heat, leading to equipment failure or damage.
Using traditional methods such as fans to cool them may not always be feasible.
Conducting heat through metal core plates for cooling is not only simple, but also an effective solution.
The working principle of conduction cooling is to transfer heat from one part of the PCB to another through directly contacting materials.
This is because it is a characteristic of heat, always moving from one hot area to another cooler area.
Thermal clad PCB consists of a metal core, dielectric material, and top and bottom copper foils.
The metal core is the most important layer in a thermal clad PCB, as it provides a low resistance heat dissipation pathway for high-power components on the PCB.
The metal core is made of materials with high thermal conductivity, such as copper or aluminum.