Circuit card assembly is a crucial step in modern electronics manufacturing, bridging the gap between design concepts and functional electronic devices. By meticulously assembling printed circuit boards and integrating their components, CCA ensures reliable and efficient operation of various electronic products. This process plays a vital role across industries, including consumer electronics, automotive systems, aerospace, and medical technology, underpinning technological advancements and product innovation.
Circuit card assembly begins with the selection of PCB materials. The choice of materials directly impacts the reliability and performance of the final product. High-density interconnect (HDI) PCBs and flexible PCBs are widely adopted in applications requiring compact design and high performance. For instance, automotive electronics demand PCBs capable of withstanding harsh environments such as extreme temperatures and vibrations. Through advanced assembly methods and automation, circuit card assembly guarantees that components are securely connected, meeting stringent performance standards.The first stage of assembly involves applying solder paste onto the PCB’s surface. This paste acts as an adhesive and electrical conductor, ensuring that components are securely attached. Precision is critical, as even minor deviations can lead to defects or performance issues. Automated solder paste printing machines play a significant role in achieving high accuracy, especially in mass production environments.
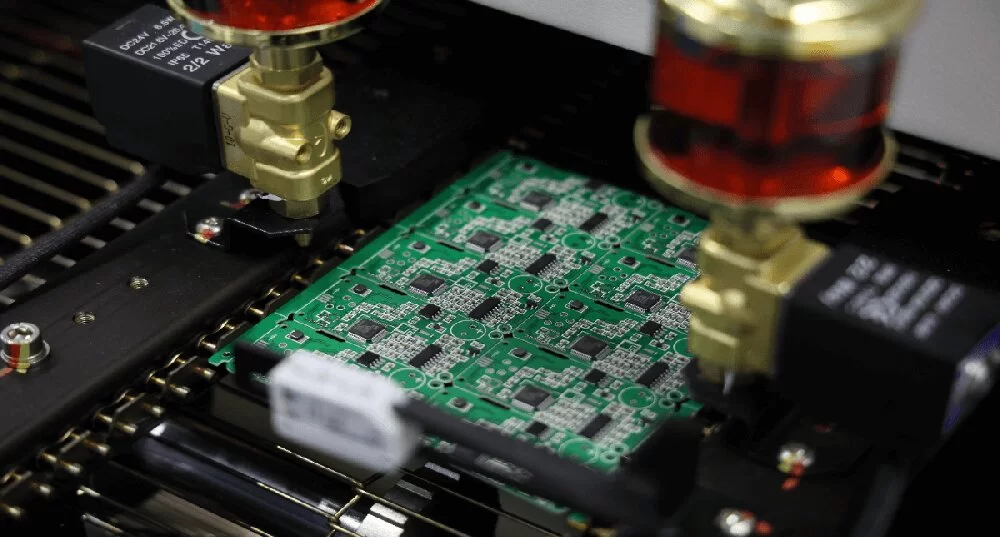
Circuit card assembly
Circuit card assembly heavily relies on surface-mount technology (SMT) to attach components to the PCB. SMT enables the placement of components directly onto the surface of the board, eliminating the need for through-hole mounting. This technology not only saves space but also enhances electrical performance by reducing parasitic inductance and capacitance.During SMT, components are positioned on the PCB with extreme precision using automated pick-and-place machines. These machines can handle thousands of components per hour, ensuring consistent quality and high throughput. Once components are placed, the PCB undergoes a reflow soldering process. In this step, the board is heated in a controlled environment, melting the solder paste and creating durable electrical connections. This process is vital for securing components and maintaining the integrity of the assembly.
Ensuring the quality of a circuit card assembly is paramount. Various testing and inspection techniques are employed to identify and rectify defects early in the manufacturing process. Automated optical inspection (AOI) systems use high-resolution cameras to examine solder joints and component placement, quickly detecting issues such as misalignment or insufficient solder.Another critical testing method is in-circuit testing (ICT), which checks the electrical performance of individual components and their connections. Flying probe testing, a non-contact method, is often used for low-volume or prototype assemblies. These advanced testing technologies improve yield rates, reduce manufacturing costs, and enhance the reliability of electronic products.
Circuit card assembly is no exception, with manufacturers adopting environmentally friendly practices and materials. Sustainability is becoming increasingly important in electronics manufacturing. The use of lead-free solder has become standard, reducing the environmental impact of electronic waste. Additionally, recyclable PCB materials are being developed to minimize waste and promote circular economy principles.Energy-efficient production processes, such as low-temperature soldering techniques, are also gaining traction. These methods reduce energy consumption during assembly without compromising quality. By prioritizing sustainability, manufacturers not only meet regulatory requirements but also contribute to global efforts in reducing carbon emissions.The demand for high-performance circuit card assemblies is growing rapidly, driven by advancements in 5G, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT). These technologies require PCBs with higher processing capabilities, greater reliability, and smaller form factors. To meet these demands, manufacturers are exploring innovative assembly techniques, such as additive manufacturing and advanced material science.
Circuit card assembly is a cornerstone of modern electronics manufacturing, enabling the creation of reliable and high-performance electronic devices. From the initial selection of materials to the final testing and inspection, every step of the assembly process is critical in ensuring product quality and functionality. As technology continues to evolve, circuit card assembly will adapt to meet new challenges and opportunities, driving innovation across industries.